Revision history [back]
 | 1 | initial version |
You can proceed as follows, where $N$ is given to serve as an approximation of $\infty$.
sage: g(x) = abs(x - floor(x) - 1/2)
sage: def f(x, N): return sum(g(2^j*x)/2^j for j in range(N+1))
sage: N = 100 # for instance...
sage: plot(f(x, N), x, -1, 1)
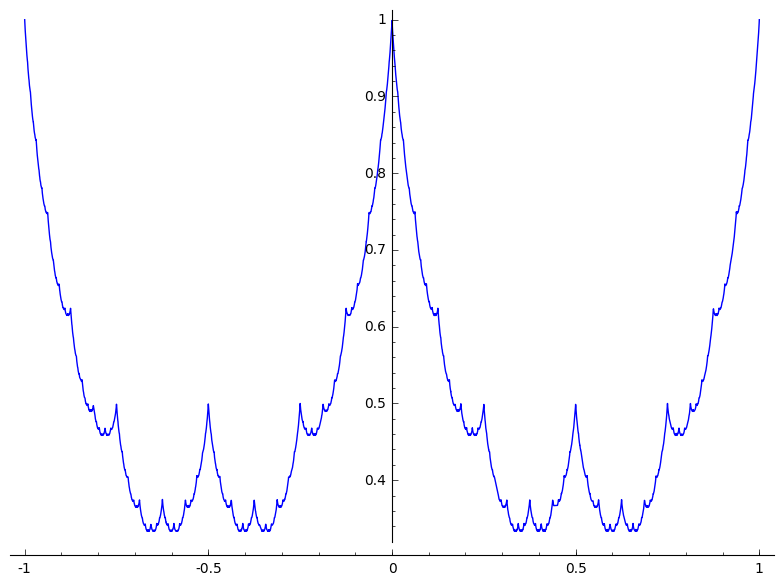
Note. For this approach to make sense, you need to show that that the partial sums converge fast, which is the case since $g(x) \le 1/2$ for all $x$.
